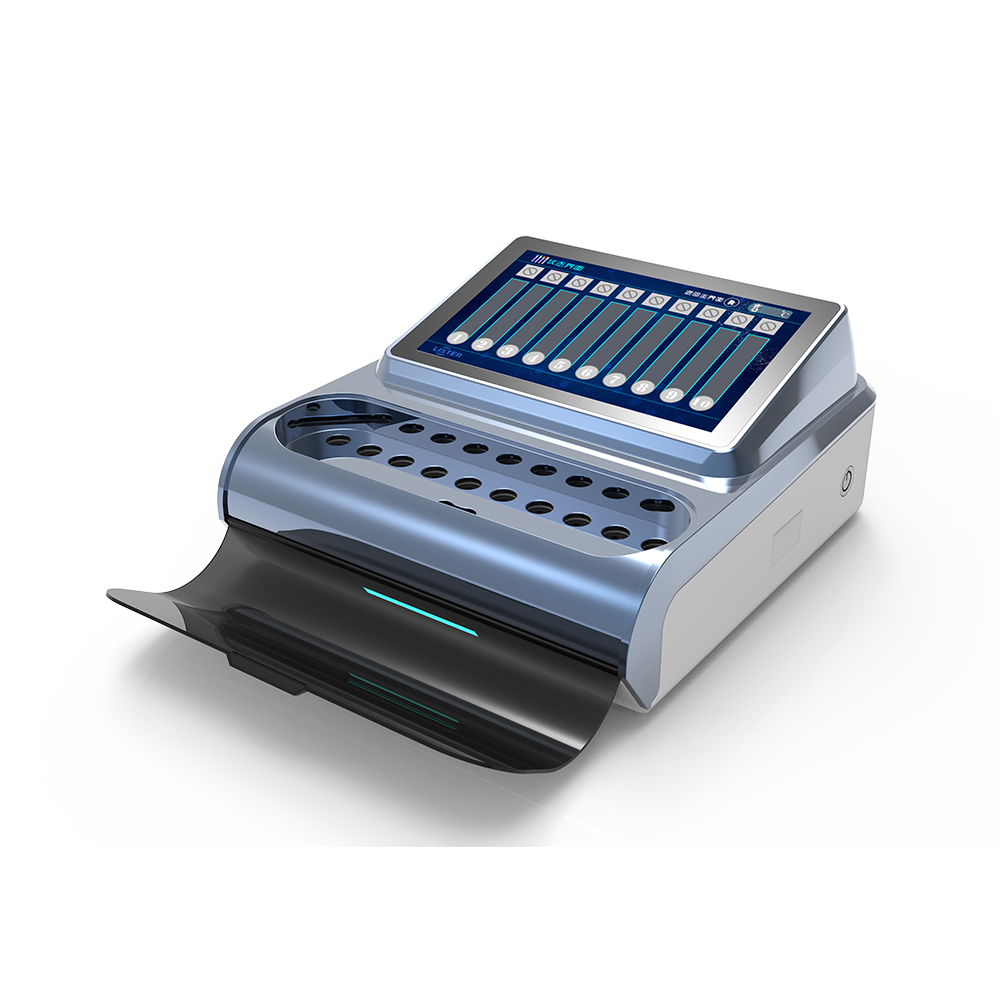
01 Jan, 2026
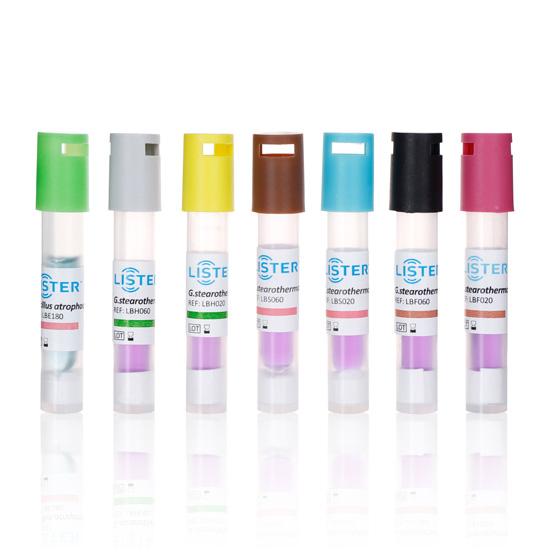
Biological indicators (BIs) are essential tools for validating sterilization processes in healthcare, pharmaceutical, and laboratory settings.
They contain highly resistant microorganisms (e.g., Geobacillus stearothermophilus for steam sterilization or
Bacillus atrophaeus for ethylene oxide) that challenge the effectiveness of sterilization equipment. Below is a
step-by-step guide to their proper use:
1. selection
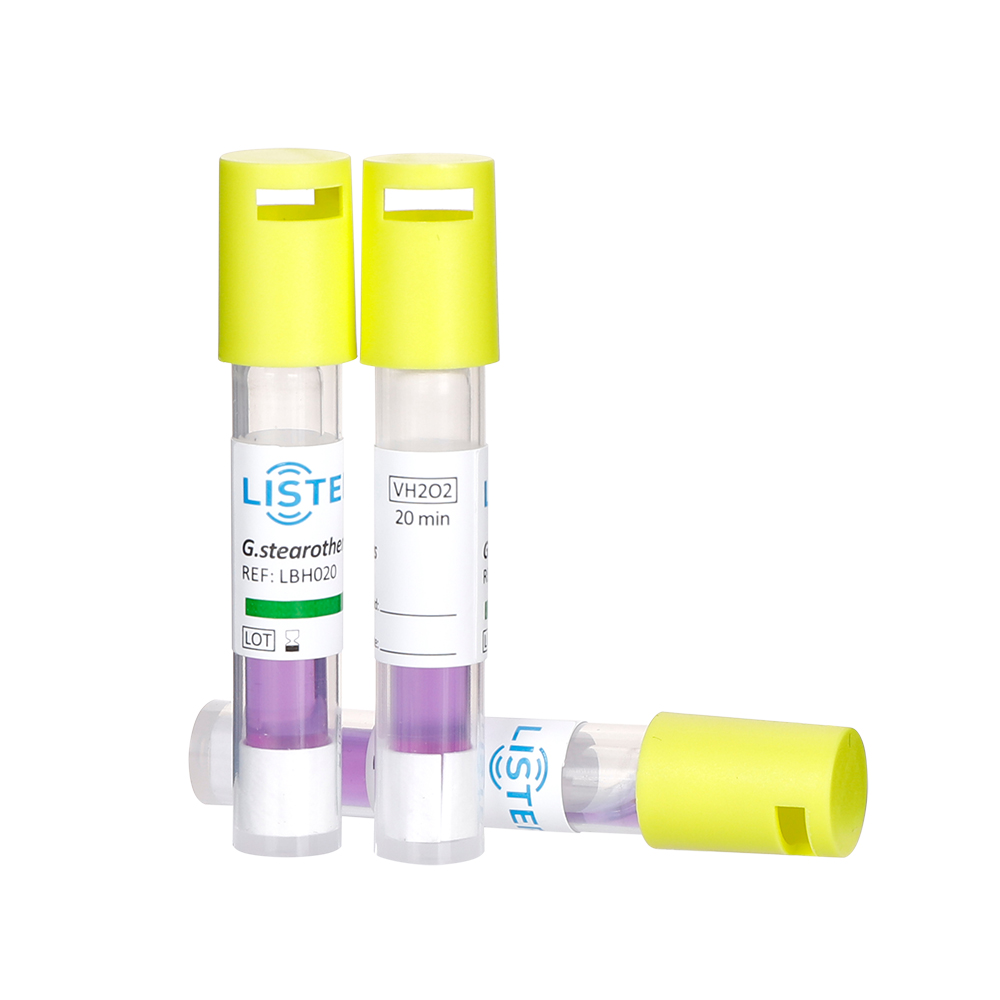
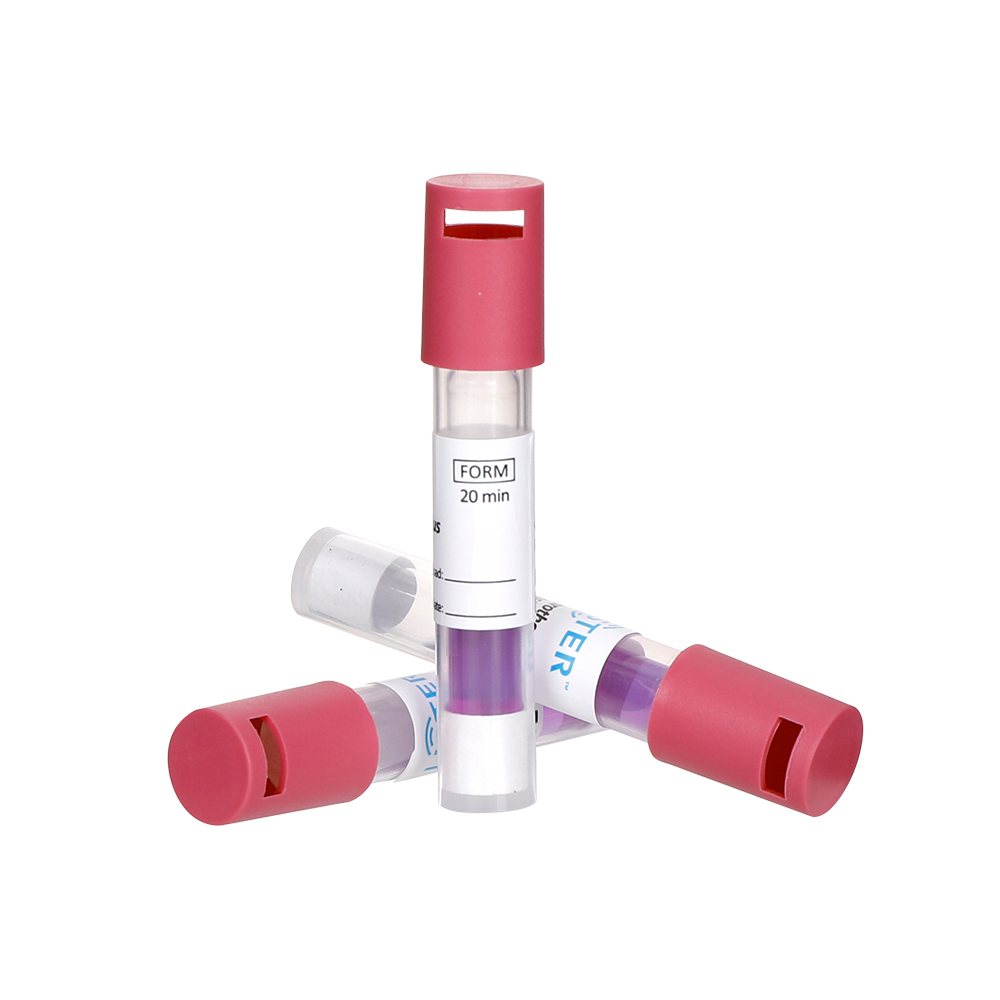
Choose a BI compatible with your sterilization method (e.g.,Steam Sterilization,EO Sterilization,VH2O2 Sterilization,
FORM Sterilization ). Common forms include spore strips, self-contained vials, or inoculated carriers.
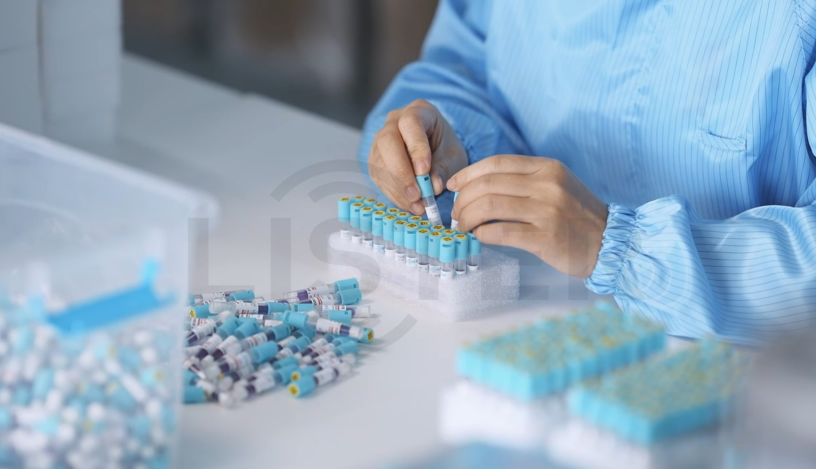
2. Placement
Position BIs in the least accessible areas of the load (e.g., center of a wrapped surgical instrument set or the
coldest spot in an autoclave). This ensures the BI tests the sterilization process’s weakest point.
3. Sterilization Cycle
Run the sterilization cycle as usual. BIs should undergo the same conditions (time, temperature, pressure, etc.)
as the rest of the load.
4. Post-Sterilization Handling
Cooling: Allow BIs to cool if exposed to high heat.
Activation: For self-contained BIs, crush the growth medium vial to hydrate the spores.
Labeling: Track each BI with batch numbers, dates, and cycle parameters.
5. Incubation
Transfer BIs to a controlled incubator at the specified temperature.
Incubate for the manufacturer-recommended time.
6. Result Interpretation
Negative Result (Sterilization PASS): No microbial growth (media remains clear).
Positive Result (Sterilization FAIL): Media turns turbid, indicating surviving spores.
Investigate sterilization parameters, equipment performance, or procedural errors.
7. Documentation
Record all BI results, including placement locations and incubation details. Retain records for compliance with
regulatory standards (e.g., FDA, ISO).
Key Considerations
Controls: Always include an unsterilized BI as a positive control to confirm spore viability.
Expiry: Use BIs within their shelf life and store them as instructed.
Safety: Handle BIs as biohazardous material until sterilization is confirmed.
By rigorously following these steps,LISTER biological indicators provide reliable evidence of sterilization efficacy,
ensuring patient safety and regulatory compliance.
Tags: